Reposted with permission from CDC’s Safe Healthcare Blog.
By Dmitry Dukhovny, MD, MPH, Associate Professor of Pediatrics at Oregon Health & Science University; Co-leader of the Northwest Neonatal Improvement Priority Alliance (NWIPA)
There are around 4 million births per year in the United States. Several hundred thousand of these infants are admitted to Neonatal Intensive Care Units (NICUs) annually because of a national prematurity rate of 9.6%, as well as 2-3% rate of congenital anomalies.
Antibiotics are one of many therapies offered to infants in these settings. However, often many infants are given antibiotics during their NICU stay without a culture-positive infection. Beyond the long-term implications of altering the newborn microbiome, evidence shows that antibiotic use has immediate side effects for NICU infants—specifically, increased risk of fungal infections and necrotizing entercolitis (NEC), both of which carry a high mortality and morbidity.
The tremendous variability in antibiotic use (overuse) in the NICU was demonstrated in 2015 in California. Schulman and colleagues demonstrated a 40-fold difference in antibiotic use (2.4-97.1% of patient days) between the California NICUs.
Much of the antibiotic use occurred in low-acuity centers. Differences in the actual rate of infections, NEC, or mortality did not explain the use patterns.

In January 2016, all 11 NICUs in Oregon and Southwest Washington partnered to form the Northwest Improvement Priority: Antibiotic Stewardship (NW IPAs) quality improvement collaborative (now named Northwest Neonatal Improvement Priority Alliance) in an effort to address antimicrobial stewardship and reduce the unnecessary antibiotic use in the NICU.
In our first year, the NW IPAs collectively reduced the antibiotic utilization rate (AUR) by about 25%. Local NICUs engaged in several projects to reduce unnecessary antibiotic use, including implementing a neonatal early-onset sepsis calculator, reducing the duration of “rule out sepsis” from 48 hours or longer to 36 hours, and implementing of hard stops into the electronic medical records. Our reductions mirror the results from the Vermont Oxford Network’s (VON) national QI cohort demonstrating that disciplined improvement is possible.
This work was done in partnership with VON’s internet-based Newborn Improvement Collaborative for Quality (iNICQ) “Choosing Antibiotics Wisely,” a national multicenter quality improvement collaborative engaging 167 NICUs nationwide.
Both groups focus on antimicrobial stewardship; VON provides an Antimicrobial Stewardship Toolkit, potentially better practices, a VON Day Audit, webinars, listservs, mentoring from experts, and web-based clinical content and training to implement disciplined quality methods training. These resources empower teams to execute effective and independent projects in the NICU. The NW IPAs also provide monthly data support, expert coaching, listserv, and ongoing webinars and face-to-face events.
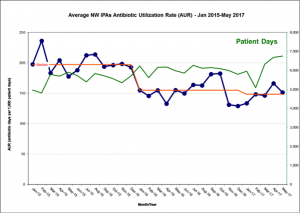
The project is currently in its second year. While all 11 NWIPA NICUs work independently, we also convene regularly to exchange ideas, learn from one another and explore opportunities for collaboration.
As CDC and VON partnered together for “iNICQ: Choosing Antibiotics Wisely” in 2017 (now extended to 2018), the NW IPAs secured support for their participation from the Healthcare Associated Infections Program of the Oregon Public Health Division with funding from the CDC Epidemiology and Laboratory Capacity Grant.
The VON iNICQ 2018 will focus on scaling the improvements made primarily in Level 3 centers, to affect every level of care, in close partnership with collaborative leaders from the NW IPAs and regional perinatal collaborative leaders in Tennessee, West Virginia, Colorado, and beyond.
This work has not only improved antibiotic stewardship, it has also formed the basis for the Neonatal Regional Quality Improvement Collaborative. The NW IPAs partner with March of Dimes, Oregon Perinatal Collaborative, Oregon Health Authority, and Oregon Pediatric Improvement Partnership and other area stakeholders to improve the health of neonates both in the short term, as well as the consequences of interventions (such as antibiotics) in the NICU on their long-term health.
On Friday, October 27, 2017, VON and CDC co-hosted a day-long Quality Improvement Symposium and Newborn Antibiotic Stewardship National Summit in Chicago, Illinois during VON’s Annual Quality Congress. More than 100 state antimicrobial stewardship program leaders came together to share, learn, and improve. Teams presented real world data and improvement stories from their collaborative work including progress on their clinical, family-centered care, and value aims.

These improvement abstracts presented along with more than 300 posters and showcased the important work done by centers who participated in “iNICQ 2017: Choosing Antibiotics Wisely.” Program attendees (including clinicians, organizational/facility leadership, educators, and data experts) share the goal of reducing the misuse and overuse of antibiotics. This collaboration is just one example of how organizations can join forces to support and strengthen one another’s antibiotic stewardship efforts.
For more information on VON iNICQ Choosing Antibiotics Wisely Collaborative: https://public.vtoxford.org/quality-education/inicq-2018/
Neonatal Early-Onset Sepsis Calculator: https://neonatalsepsiscalculator.kaiserpermanente.org/
Publication by Schulman et al. in Pediatrics 2015 on NICU antibiotic use: http://pediatrics.aappublications.org/content/135/5/826.long
Dmitry Dukhovny, MD, MPH, is an associate professor of pediatrics at Oregon Health & Science University and one of the co-founders and co-leaders of the Northwest Neonatal Improvement Priority Alliance (NWIPA), a regional quality improvement collaboration amongst all11 Neonatal Intensive Care Units in Oregon and Southern Washington. He is also currently on faculty for the ongoing Vermont Oxford Network (VON) internet-based quality improvement collaborative “Choosing Antibiotics Wisely.”